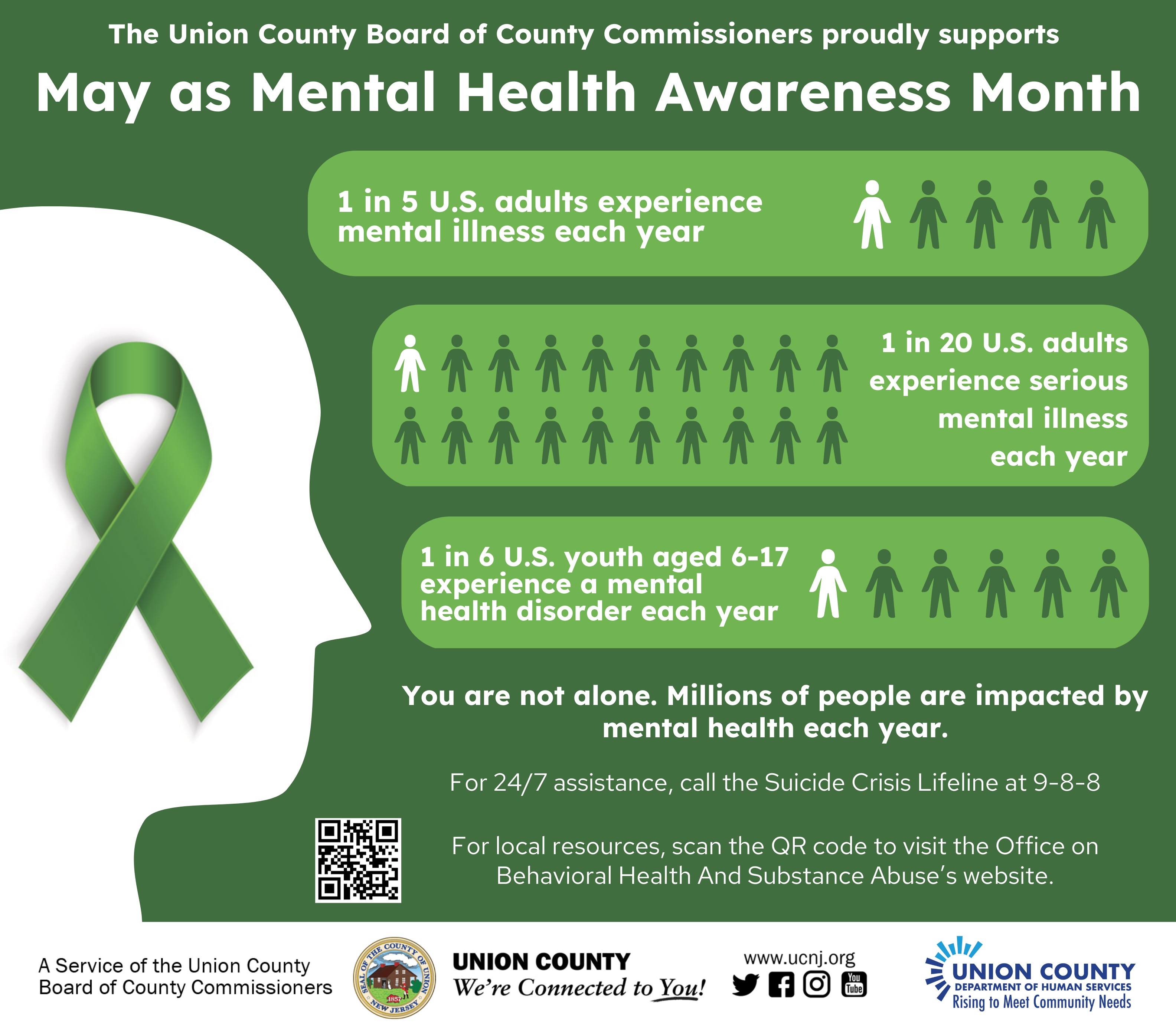
As Mental Health Awareness Month commences, let’s embark on a journey to destigmatize mental health and promote well-being. Together, we can create a more understanding and supportive society where individuals can seek help without shame or fear.
Mental health disorders affect millions worldwide, impacting individuals, families, and communities. This month, we raise awareness, challenge stigma, and advocate for accessible and affordable mental healthcare for all.
Mental Health Awareness Month Overview
Mental Health Awareness Month is an annual observance held in May to raise awareness of mental health issues and promote the importance of mental well-being. It was first established in 1949 as Mental Health Week by the National Association for Mental Health (NAMH) and has since grown into a month-long campaign.
Mental health disorders affect millions of people worldwide, causing significant personal, social, and economic burdens. They can impact individuals’ thoughts, feelings, and behaviors, leading to difficulties in daily life, relationships, and overall well-being. Raising awareness about mental health helps reduce stigma, promote understanding, and encourage individuals to seek help when needed.
History
The history of Mental Health Awareness Month can be traced back to 1949 when the National Association for Mental Health (NAMH) launched Mental Health Week. The goal was to raise public awareness about mental illness and dispel the stigma associated with it. Over the years, the observance has evolved into a month-long campaign, with various organizations, government agencies, and individuals participating to promote mental health awareness.
Significance
Mental Health Awareness Month holds great significance in promoting mental well-being and reducing the stigma surrounding mental health issues. It provides an opportunity to educate the public about the prevalence, causes, and treatments for mental health disorders. By raising awareness, we can encourage individuals to seek help when needed and foster a more supportive and understanding environment for those affected by mental health challenges.
Goals
The primary goals of Mental Health Awareness Month include:
- Raising awareness about mental health issues and their impact on individuals, families, and communities.
- Reducing the stigma associated with mental illness and promoting understanding and acceptance.
- Encouraging individuals to seek help when needed and providing information about available resources.
- Advocating for policies and programs that support mental health and well-being.
Prevalence and Impact of Mental Health Issues
Mental health issues affect a significant portion of the global population, impacting individuals, families, and society as a whole. Understanding the prevalence and impact of these conditions is crucial for raising awareness and implementing effective interventions.
Prevalence of Mental Health Issues
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), an estimated 1 in 4 people globally will experience a mental health condition in their lifetime. This includes disorders such as depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia.
The prevalence of mental health issues varies across different regions and demographics. In developed countries, for example, anxiety disorders are the most common, while in developing countries, depression is more prevalent.
Impact of Mental Health Conditions
Mental health conditions can have a profound impact on individuals, families, and society.
- Individuals: Mental health issues can impair daily functioning, affect relationships, and lead to decreased quality of life.
- Families: Caring for a loved one with a mental health condition can be stressful and emotionally draining for family members.
- Society: Mental health issues can contribute to lost productivity at work, increased healthcare costs, and social stigma.
Recognizing the prevalence and impact of mental health issues is essential for destigmatizing these conditions and promoting access to appropriate care and support.
Stigma and Discrimination Associated with Mental Health
Mental health issues are often stigmatized, leading to discrimination and negative consequences for individuals seeking help and accessing treatment.
Stigma arises from misunderstandings, misinformation, and negative attitudes towards mental illness. Individuals with mental health conditions may face prejudice, judgment, and social exclusion, which can significantly impact their well-being.
Consequences of Stigma
- Reluctance to Seek Help: Stigma can prevent individuals from seeking professional help due to fear of being labeled, judged, or discriminated against.
- Delayed Diagnosis and Treatment: As a result of stigma, individuals may delay seeking help, leading to delayed diagnosis and treatment, which can worsen their condition.
- Social Isolation: Stigma can lead to social isolation, as individuals may withdraw from social interactions to avoid being stigmatized.
- Employment Discrimination: Individuals with mental health conditions may face discrimination in the workplace, including job loss, denial of promotions, and workplace harassment.
- Negative Self-Perception: Stigma can negatively impact individuals’ self-perception, leading to feelings of shame, low self-esteem, and hopelessness.
Raising Awareness and Promoting Understanding
Addressing mental health issues requires collective effort. Raising awareness and fostering understanding play a pivotal role in reducing stigma and promoting empathy. By educating ourselves and others, we can challenge misconceptions, create a supportive environment, and encourage individuals to seek help when needed.
Effective Strategies for Reducing Stigma and Fostering Empathy
- Open and Honest Conversations: Encourage open discussions about mental health, reducing the taboo associated with it. Share personal experiences, listen attentively to others, and promote understanding.
- Media Representation: Portrayals of mental health issues in the media should be accurate, sensitive, and non-stigmatizing. Positive and relatable representations can help normalize mental health experiences and reduce the perception of weakness.
- Educational Programs: Implement educational programs in schools, workplaces, and communities to provide factual information about mental health, its prevalence, and available support services.
li>Anti-Stigma Campaigns: Launch public awareness campaigns to challenge stereotypes and promote acceptance of individuals with mental health conditions.
Access to Mental Health Services
Access to mental health services remains a significant challenge worldwide, with many individuals facing barriers to care. The availability of services varies widely across regions and countries, and even within countries, disparities exist in urban and rural areas.
Barriers to Accessing Care
- Stigma and discrimination: Fear of judgment and negative attitudes can prevent individuals from seeking help.
- Lack of awareness: Many people are unaware of mental health conditions and the services available.
- Financial barriers: Mental health services can be expensive, and many individuals lack insurance coverage.
- Limited availability: In some areas, there is a shortage of mental health professionals, leading to long wait times and limited access to care.
Solutions to Improve Service Delivery
- Increase funding: Governments and healthcare organizations should invest more in mental health services to expand availability and reduce costs.
- Reduce stigma: Public education campaigns and anti-discrimination laws can help reduce stigma and encourage individuals to seek help.
- Train more mental health professionals: Expanding the workforce can help meet the growing demand for services.
- Utilize technology: Telehealth and online therapy platforms can increase accessibility for individuals in remote areas or with transportation challenges.
- Integrate mental health services into primary care: Screening and brief interventions in primary care settings can identify and address mental health issues early on.
Role of Technology in Mental Health Care

Technology is rapidly transforming the healthcare landscape, and mental health care is no exception. The use of technology in mental health care, often referred to as “telehealth” or “e-mental health,” offers numerous potential benefits, including increased access to care, reduced stigma, and improved outcomes.
One of the most significant benefits of technology in mental health care is its ability to increase access to care. Many people with mental health conditions face barriers to accessing traditional in-person therapy, such as transportation challenges, geographic isolation, or lack of insurance coverage. Telehealth can help to overcome these barriers by providing remote access to mental health services, making it more convenient and affordable for people to get the help they need.
Telemedicine
Telemedicine is the use of video conferencing or other electronic communication technologies to provide remote medical care. In the context of mental health, telemedicine can be used to provide therapy, counseling, and other mental health services. Telemedicine has been shown to be effective in treating a wide range of mental health conditions, including depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Online Therapy
Online therapy is a type of mental health care that is delivered over the internet. Online therapy platforms typically offer a variety of services, including video conferencing, chat-based therapy, and self-guided programs. Online therapy can be a convenient and affordable option for people who are unable to access in-person therapy or who prefer the convenience of receiving care from home.
Mobile Health Apps
Mobile health (mHealth) apps are another way to deliver mental health care using technology. MHealth apps can provide a variety of services, including symptom tracking, self-management tools, and access to mental health professionals. MHealth apps can be a valuable complement to traditional mental health care, and they can help people to manage their mental health conditions on a daily basis.
Self-Care and Prevention Strategies
Maintaining good mental well-being and preventing mental health issues require proactive self-care and preventative measures. These strategies empower individuals to manage their mental health proactively, reducing the likelihood of developing severe conditions.
Importance of Self-Care, Mindfulness, and Building Resilience
Self-care encompasses practices that nurture physical, emotional, and mental well-being. Engaging in self-care activities regularly helps individuals cope with stress, improve mood, and enhance overall well-being.
Mindfulness is a technique that involves paying attention to the present moment without judgment. Practicing mindfulness can reduce stress, improve focus, and increase self-awareness.
Resilience refers to the ability to adapt and bounce back from challenges. Building resilience involves developing coping mechanisms, maintaining a positive outlook, and seeking support when needed.
Self-Care Practices
- Meditation
- Yoga
- Spending time in nature
- Engaging in hobbies
- Connecting with loved ones
- Getting enough sleep
- Eating a healthy diet
- Exercising regularly
Benefits of Mindfulness
- Reduces stress
- Improves focus
- Increases self-awareness
- Enhances emotional regulation
- Promotes better sleep
Tips for Building Resilience
- Identify your strengths and weaknesses
- Develop coping mechanisms
- Maintain a positive outlook
- Seek support when needed
- Learn from your experiences
- Practice self-compassion
Advocacy and Policy Initiatives: Mental Health Awareness Month
Mental health advocacy plays a vital role in raising awareness, challenging stigma, and improving mental health outcomes. Through advocacy efforts and policy initiatives, individuals, organizations, and governments work together to create a more supportive and equitable environment for individuals with mental health conditions.
Role of Advocacy in Mental Health, Mental Health Awareness Month
Advocacy involves speaking out, educating the public, and influencing policy decisions to promote mental health awareness and access to care. By raising awareness, advocates challenge misconceptions and reduce stigma associated with mental health issues, fostering a more inclusive society.
Policy Initiatives and Their Impact
Policy initiatives, such as the Mental Health Parity Act and the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline, have significantly improved access to mental health care and reduced suicide rates. These initiatives ensure that insurance plans cover mental health services on par with physical health services, providing financial relief and reducing barriers to care.
Challenges and Opportunities for Advocacy
Despite progress, challenges remain in mental health advocacy. Funding for mental health services often falls short, and stigma continues to hinder individuals from seeking help. However, opportunities exist to expand access to care through telehealth, peer support programs, and community-based initiatives.
Cultural and Social Factors Influencing Mental Health

Mental health is shaped not only by individual factors but also by broader cultural and social contexts. These factors can influence the prevalence, expression, and treatment of mental health issues.
Cultural influences, such as beliefs, values, and norms, can impact how individuals perceive and respond to mental health. In some cultures, mental health issues may be stigmatized or seen as a sign of weakness, leading to underreporting and delayed treatment. Conversely, other cultures may have more supportive and understanding attitudes towards mental health, promoting help-seeking behaviors.
Socioeconomic Status
Socioeconomic status is closely linked to mental health outcomes. Individuals from lower socioeconomic backgrounds tend to have higher rates of mental health issues due to factors such as poverty, limited access to healthcare, and exposure to stressors like unemployment, housing instability, and discrimination.
Social Support
Social support plays a crucial role in mental well-being. Strong social networks can provide individuals with emotional support, a sense of belonging, and access to resources. Conversely, lack of social support can increase the risk of mental health issues, particularly in times of stress.
Importance of Addressing Disparities and Promoting Inclusivity
Recognizing and addressing mental health disparities is essential for promoting equitable access to care and improving overall mental health outcomes. Efforts should focus on reducing stigma, increasing awareness, and providing culturally competent and inclusive services that meet the unique needs of diverse populations.
Role of Media in Shaping Mental Health Perceptions
The media plays a pivotal role in shaping public perceptions and attitudes towards mental health. Responsible reporting practices and accurate representation are crucial to dispel misconceptions, reduce stigma, and promote understanding.
Media Campaigns for Mental Health Awareness
Effective media campaigns have successfully raised awareness about mental health issues and reduced stigma. The “Time to Change” campaign in the UK employed powerful personal stories to challenge stereotypes and promote empathy.
Social Media’s Impact on Mental Health Perceptions
Social media platforms can have both positive and negative effects on mental health. On the one hand, they can provide support, information, and a sense of community. On the other hand, they can also contribute to cyberbullying, comparison, and unrealistic expectations.
Mental Health in the Workplace
Mental health issues are prevalent in the workplace, affecting both individuals and organizations. Understanding their impact and implementing strategies to promote mental well-being is crucial for creating a supportive and productive work environment.
Prevalence and Impact
Mental health conditions, such as anxiety, depression, and stress, are common among employees. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), an estimated 26% of working-age adults worldwide experience mental health problems.
- Mental health issues can lead to absenteeism, reduced productivity, and increased healthcare costs.
- They can also impact employee morale, job satisfaction, and overall well-being.
Promoting Mental Well-being
Organizations can take proactive steps to promote mental well-being in the workplace.
- Create a supportive culture: Foster an environment where employees feel comfortable discussing mental health concerns and seeking support.
- Provide access to resources: Offer employee assistance programs, mental health screenings, and counseling services.
- Encourage work-life balance: Implement flexible work arrangements, paid time off, and stress management programs to prevent burnout.
Successful Interventions
Numerous successful interventions have been implemented to improve mental health in the workplace.
- Mindfulness training: Teaching employees mindfulness techniques has been shown to reduce stress and improve emotional regulation.
- Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT): CBT helps employees identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to mental health issues.
li>Peer support programs: Connecting employees with colleagues who have similar experiences can provide a sense of community and reduce stigma.
Role of Technology
Technology can play a valuable role in promoting mental health in the workplace.
- Mental health apps: These apps offer self-help tools, such as guided meditations, CBT exercises, and mood tracking.
- Telehealth services: Employees can access mental health services remotely, increasing accessibility and convenience.
Remote Work and Mental Health
The rise of remote work has had a significant impact on mental well-being.
- Benefits: Increased flexibility, reduced commuting stress, and improved work-life balance can positively impact mental health.
- Challenges: Isolation, lack of social interaction, and blurred work-life boundaries can contribute to mental health issues.
Mental Health in Schools and Educational Settings
Educational institutions play a crucial role in shaping the mental well-being of students and educators. Schools can be a source of stress, anxiety, and depression for some individuals, while also providing opportunities for social connection, emotional support, and the development of coping mechanisms.
It is essential to recognize the mental health needs of both students and educators and implement comprehensive programs and initiatives to promote mental well-being and prevent mental health issues.
School-Based Programs and Initiatives
Effective school-based mental health programs can include:
- Mental health education and awareness campaigns
- Counseling and support services
- Peer support groups
- Teacher training on mental health issues
- School-wide policies and procedures to support students with mental health needs
These programs can help to create a supportive and inclusive school environment, reduce stigma, and provide students and educators with the resources they need to thrive.
Mental Health and Physical Health Connection

Mental and physical health are inextricably linked, forming a bidirectional relationship. Physical health conditions can contribute to mental health issues, while mental health conditions can impact physical well-being.
Physical Health Conditions Contributing to Mental Health Issues
- Chronic illnesses (e.g., cancer, heart disease) can lead to anxiety, depression, and fatigue.
- Pain and discomfort can disrupt sleep, impair concentration, and increase irritability.
- Neurological disorders (e.g., Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s) can affect cognitive function, mood, and behavior.
Mental Health Conditions Contributing to Physical Health Issues
- Depression and anxiety can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease, stroke, and diabetes.
- Chronic stress can suppress the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections.
- Mental health disorders can interfere with healthy behaviors (e.g., exercise, nutrition), further compromising physical health.
Importance of Integrating Mental Health Care into Overall Healthcare Systems
Integrating mental health care into healthcare systems is crucial due to:
- Improved patient outcomes: Addressing mental health needs can enhance overall well-being and reduce the risk of physical health complications.
- Reduced healthcare costs: Early intervention and treatment of mental health issues can prevent more severe conditions and associated medical expenses.
- Increased access to care: Integration makes mental health services more accessible and reduces stigma associated with seeking help.
Strategies for Integrating Mental Health Care
- Establish collaborative care models between primary care providers and mental health professionals.
- Train healthcare providers on recognizing and addressing mental health issues.
- Implement screening programs for mental health disorders in primary care settings.
- Provide telehealth services to increase accessibility and reduce transportation barriers.
Examples of Interconnectedness
* Stress from work or relationships can lead to headaches, muscle tension, and gastrointestinal problems.
* Depression can disrupt sleep patterns, resulting in fatigue and impaired cognitive function.
* Chronic pain can contribute to anxiety, irritability, and sleep disturbances.
Summary
The connection between mental and physical health is undeniable, highlighting the need for a holistic approach to healthcare. Integrating mental health care into overall healthcare systems improves patient outcomes, reduces costs, and increases access to essential services. Recognizing and addressing the bidirectional relationship between mental and physical health is crucial for promoting overall well-being and achieving optimal health outcomes.
Future Directions and Innovations in Mental Health Care
The field of mental health care is constantly evolving, with new trends and innovations emerging all the time. These innovations have the potential to revolutionize the way that mental health is diagnosed, treated, and prevented. In this section, we will explore some of the most promising emerging trends and innovations in mental health care, and discuss their potential impact on the future of mental health treatment and prevention.
Personalized Treatments
One of the most important trends in mental health care is the move towards personalized treatments. This means that treatment plans are tailored to the individual needs of each patient, taking into account their unique symptoms, history, and preferences. Personalized treatments have been shown to be more effective than traditional one-size-fits-all approaches, and they can help patients to achieve better outcomes.
- Example: Precision medicine is a type of personalized treatment that uses genetic information to tailor treatment plans to the individual needs of each patient.
- Example: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a type of therapy that has been shown to be effective for a wide range of mental health conditions. However, CBT can be tailored to the individual needs of each patient, making it even more effective.
Ultimate Conclusion

Mental Health Awareness Month serves as a reminder that mental health is just as important as physical health. By fostering open conversations, providing support, and advocating for resources, we can empower individuals to live fulfilling lives free from the burden of mental illness.
FAQ Section
What is the significance of Mental Health Awareness Month?
It’s an opportunity to raise awareness, reduce stigma, and promote mental well-being by encouraging open conversations and advocating for accessible mental healthcare.
How can I support someone with a mental health condition?
Offer empathy, listen without judgment, encourage professional help, and respect their boundaries.
What are the common signs of mental health issues?
Changes in mood, sleep, appetite, energy levels, concentration, and social withdrawal can indicate potential mental health concerns.